What Is Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin Made From?
Derived from Renewable Raw Materials Such as Corn, Sugarcane, or Cellulose
Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is made from renewable raw materials like corn, sugarcane, or cellulose. These natural sources are rich in carbohydrates, which can be converted into bio-based monomers that are then polymerized into resins. Unlike traditional petroleum-based resins, which rely on non-renewable fossil fuels, bio-based resins utilize raw materials that can be replenished over time, making them a more sustainable alternative.
The use of renewable materials not only helps reduce the environmental impact but also encourages the use of agricultural waste or by-products, contributing to a more circular and sustainable economy. Bio-based resins are an important step towards reducing dependence on fossil fuels and advancing environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
Contrast with Petroleum-Based Resins
Petroleum-based resins are derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, primarily crude oil. These resins are widely used in various industries due to their versatile properties and cost-effectiveness. However, the production of petroleum-based resins involves high carbon emissions, contributing to environmental degradation and climate change. Additionally, the extraction and refinement of petroleum have negative environmental consequences, including habitat destruction and pollution.
On the other hand, bio-based environmentally friendly resins reduce the carbon footprint associated with production, as the renewable materials used in their creation absorb carbon during their growth phase. This makes them a greener and more sustainable choice for many applications.
Explanation of the Chemical Process Behind Bio-Resin Production
The production of Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin begins with the extraction of carbohydrates from renewable raw materials such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose. These raw materials undergo a series of chemical processes, including fermentation and polymerization, to create the monomers needed for resin production.
Fermentation: The carbohydrates are fermented into monomers like lactic acid, which is commonly used in bio-based resins like polylactic acid (PLA).
Polymerization: The monomers are then polymerized to form long chains, creating the resin. This resin can be further processed into various products, including films, coatings, and molded parts.
Cross-Linking: In some bio-resins, a process known as cross-linking is used to enhance the resin's strength, flexibility, and resistance to heat.
This chemical process allows bio-based resins to maintain similar or even superior properties compared to petroleum-based resins while offering a more sustainable production method. The key advantage of bio-resins is their ability to be manufactured using renewable resources, reducing the environmental impact of their production and use.
Where Can Bio-Based Resin Be Applied?
Packaging Industry: Biodegradable Alternatives to Plastic
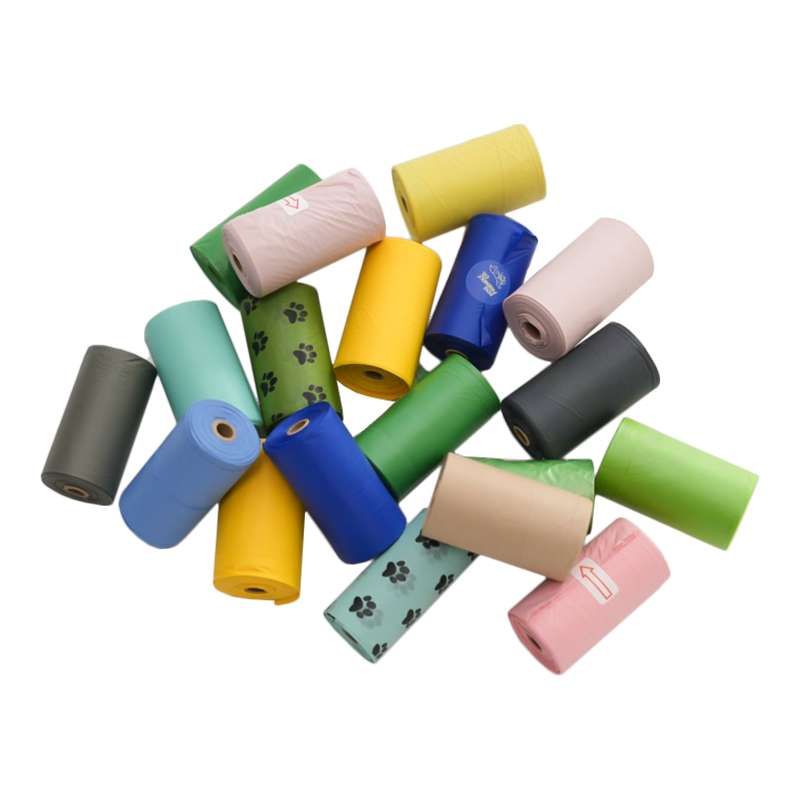
One of the most promising applications of Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is in the packaging industry. With growing concerns over plastic pollution, bio-based resins offer a sustainable alternative. These resins can be used to produce biodegradable packaging materials that break down naturally in the environment, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of packaging materials.
Bio-based resins are commonly used to create films, bottles, and food packaging. Materials like PLA (polylactic acid) are used for products such as food containers and biodegradable bags, which are designed to decompose naturally over time, unlike traditional plastic packaging that can persist in the environment for centuries.
Automotive: Lightweight and Eco-Friendly Interior Components
In the automotive industry, Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is being used to create lightweight, eco-friendly interior components. These resins are ideal for automotive applications because they can be molded into complex shapes, are durable, and reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, leading to better fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
Bio-based resins are used in parts such as door panels, seat covers, dashboard components, and insulation materials. By replacing petroleum-based plastics with bio-resins, the automotive industry is moving towards a more sustainable future, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact.
Construction: Sustainable Adhesives and Coatings
The construction industry is another area where Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is making a significant impact. Bio-resins are used in sustainable adhesives and coatings, which are important for reducing the carbon footprint of building materials. These eco-friendly resins are used in products like paints, varnishes, and construction adhesives, which contribute to greener buildings and homes.
Bio-resins offer excellent adhesion, durability, and resistance to weathering, making them ideal for construction applications. Additionally, they are non-toxic and have low VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions, which makes them safer for both the environment and the people who live and work in the buildings constructed with them.
Electronics: Reducing Carbon Footprint in Casings and Parts
In the electronics industry, Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is being increasingly used to replace traditional plastic in the production of casings and components. The use of bio-resins in electronics helps reduce the carbon footprint of these products by incorporating renewable raw materials into their construction.
Bio-based resins are used to create durable, lightweight casings for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and televisions. By utilizing bio-resins, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on petroleum-based plastics and make their products more environmentally friendly while still maintaining the performance and quality expected from electronic devices.
What Advantages Does Bio-Based Resin Offer Compared to Traditional Resins?
Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions During Production
The production of Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin results in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional petroleum-based resins. Since bio-resins are derived from renewable resources, the overall carbon footprint of their production is significantly reduced. The cultivation of raw materials like corn and sugarcane also helps absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making the production process even more sustainable.
Biodegradability and Compostability
One of the key benefits of Bio-Based Environmentally Friendly Resin is its biodegradability. Unlike traditional plastics that can take hundreds of years to decompose, bio-resins break down naturally in the environment, reducing long-term waste. Many bio-resins are also compostable, meaning they can be safely disposed of in composting facilities, turning into organic material without harming the environment.
Similar or Enhanced Performance Properties
Bio-resins are designed to have similar, if not superior, performance properties compared to traditional resins. They can match the strength, flexibility, and durability of petroleum-based resins, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. In fact, some bio-resins offer enhanced properties, such as improved impact resistance or higher temperature tolerance, making them ideal for demanding industries like automotive and electronics.