What is Fully Biodegradable Polyester Modified Material? How does it stand out among environmentally friendly plastics?
Fully biodegradable polyester modified material is a new type of environmentally friendly material based on fully degradable polyester and optimized for performance. These materials can be degraded into water, carbon dioxide and biomass through microbial action under natural conditions, and will not form residual microplastics in the ecological environment. They are sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics. The so-called "modification" refers to the use of technical means (such as blending, toughening, filling, grafting, etc.) to improve its processability, mechanical properties, thermal stability, etc., so that the material can better adapt to the needs of actual application scenarios on the basis of meeting environmental performance.
Among traditional biodegradable materials, PLA has good rigidity and transparency, but is brittle and has poor thermal stability; PBAT has good flexibility and can be blown into film, but has high cost and average strength; PBS has good thermal stability and crystallinity, but poor film-forming properties. Through scientific modification formula design, their advantages can be complemented, and different performance indicators can be adjusted according to product uses.
What are the types of fully biodegradable polyester modified materials? How are their performance and application scenarios classified?
Fully biodegradable polyester modified materials cover multiple different types. According to the base resin, modification method and final use, they can be divided into a variety of performance formulas and application directions. Generally, they can be classified from the following dimensions:
A. Classification by base material
PBAT modified type: PBAT is the main material, with excellent flexibility and blown film properties, suitable for shopping bags, garbage bags, express packaging bags, etc. The film-forming properties and cost control are enhanced by adding PLA or starch.
PLA modified type: PLA is the main material, with good transparency and strength, suitable for food packaging, straws, lunch boxes, etc., but toughening agents are needed to improve its impact resistance.
PBS modified type: PBS is used as the matrix, suitable for agricultural film, seedling pots, thermoforming products and other scenarios, and has excellent thermal stability and aging resistance after modification.
B. Classification by modification direction
Toughened modified materials: used to improve the toughness of PLA and PBS and improve their brittleness.
Filling modified materials: Add natural ingredients such as starch and calcium powder to reduce costs, increase degradation speed, and retain necessary mechanical properties.
Multifunctional composite materials: Through a combination of various polyesters, it takes into account mechanical, thermal, biodegradable and other aspects of performance, suitable for customized customers.
C. Classification by application scenario
Packaging field: used for food bags, packaging films, bubble bags, etc., requiring transparency and good heat sealing performance.
Agricultural use: such as agricultural films, seedling trays, and controlled-release fertilizer coatings, which need to have weather resistance and controllable degradation cycles.
Daily necessities and disposable products: such as degradable tableware, cup lids, straws, etc., need to meet the requirements of safety, heat resistance and rapid degradation.
What are the environmental advantages of using fully biodegradable polyester modified material? How does it contribute to sustainable development?
The biggest environmental advantage of fully biodegradable polyester modified material lies in its "green closed loop throughout the life cycle". From the selection of raw materials to the disposal of products, it has the ability to reduce carbon emissions, reduce pollution, and be sustainable, which is particularly in line with the current global trend of "green and low-carbon" economic transformation.
Most of these materials come from renewable resources, such as corn starch, sugar cane, cassava, vegetable oil and other biomass, which can reduce dependence on petrochemical resources at the source. Compared with traditional plastics, their manufacturing process has lower carbon emissions and a smaller carbon footprint, which helps companies achieve ESG goals and carbon neutrality commitments.
After the product is used, these materials can be decomposed by microorganisms in a composting environment, soil or ocean to produce water and carbon dioxide, without any residual harmful substances or microplastics. This "natural degradation" model greatly reduces the environmental pressure of "white pollution" and also reduces the burden on urban garbage classification and treatment.
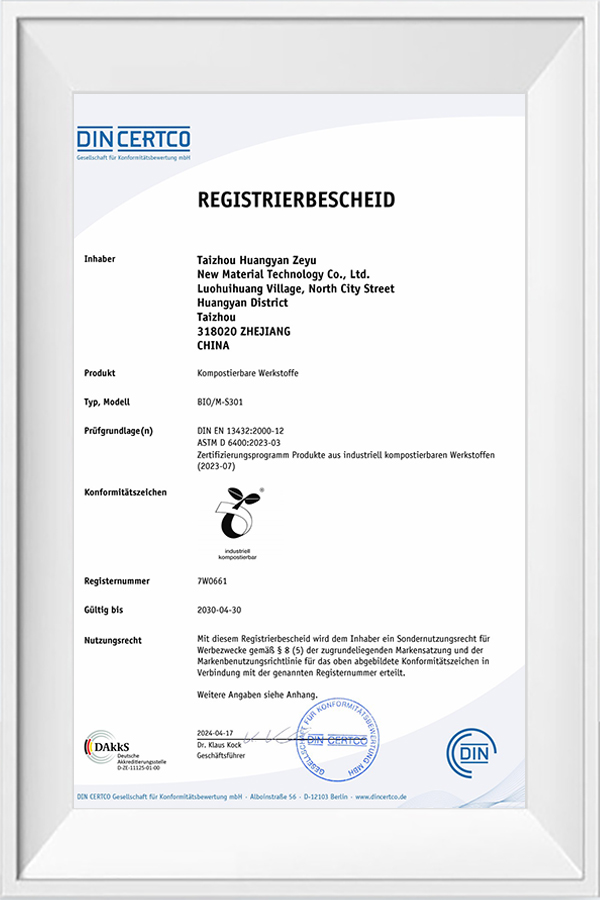
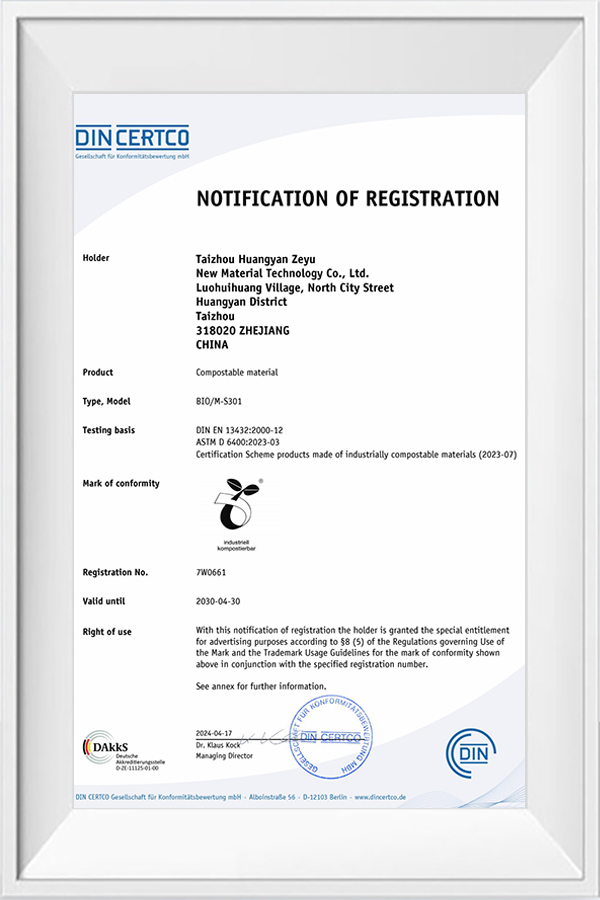
Taizhou Huangyan Zeyu New Material Technology Co., Ltd. clearly puts forward the research and development orientation of "sustainable raw materials" at the corporate strategic level, and insists on developing modified products that comply with environmental regulations. Through technological innovation and product upgrades, the company not only provides customers with green, efficient and degradable packaging solutions, but also promotes the entire industry chain to develop in a more sustainable and responsible direction.