What is PLA? What are its main characteristics and classification applications?
PLA is a bio-based polyester material based on renewable resources. It is mainly made of sugars from natural plants such as corn starch, cassava, and sugarcane, which are fermented by microorganisms to produce lactic acid and then polymerized. As a new generation of environmentally friendly plastics, PLA not only comes from nature, but also returns to nature naturally, and has significant environmental value.
The core characteristics of PLA include the following aspects:
Strong renewability: PLA's raw materials are taken from agricultural by-products or specially planted starch crops, and the resource sources are extensive, which ensures the sustainability of its raw materials.
Biodegradability: Under certain humidity, temperature and microbial action, PLA can be degraded into water and carbon dioxide within 6 to 12 months, avoiding the "white pollution" caused by traditional plastics.
Good transparency and appearance texture: PLA has transparency and rigidity similar to PET, and is suitable for display food packaging.
Good processing performance: PLA has a low melting point (about 150-170℃), and is easy to be molded and produced through traditional plastic processes such as injection molding, film blowing, and extrusion.
Good biocompatibility: non-toxic to the human body, suitable for medical devices, food contact materials and other applications with high safety requirements.
Depending on the application field, common classification products of PLA materials include:
Food packaging: such as PLA cling film, transparent boxes, take-out boxes, etc., suitable for cold food and fresh food packaging, with anti-seepage, transparency and degradation characteristics.
Disposable tableware: PLA knives, forks, spoons, straws, cups are widely used in fast food industry, airline catering, cafes, etc., replacing traditional petrochemical plastics and conforming to the "plastic restriction" trend.
Medical and sanitary products: such as disposable syringe shells, sutures, dressings, etc., with their biocompatibility and degradability, have broad prospects in the medical field.
Textile and non-woven products: PLA fibers can be used in environmentally friendly clothing, baby products, sanitary napkins, masks, etc., with the advantages of softness, breathability, skin-friendly and non-irritating.
Why can PLA become an important representative of environmentally friendly materials? What is its industrial value and development potential?
In the context of dealing with plastic pollution and promoting the "dual carbon" goal, PLA, as a bio-based degradable plastic, has become one of the key directions for the development of global green materials with its ecological advantages of "natural source and thorough degradation".
From the perspective of environmental protection attributes, the biggest advantage of PLA is its complete biodegradability. Under natural conditions or industrial composting environments, PLA can be completely decomposed by soil microorganisms without leaving any harmful substances and causing secondary pollution to water, soil or air. This "green life cycle" feature enables PLA to effectively replace disposable plastic products and play an important role in high-frequency consumption scenarios such as catering, packaging, and medical care.
The industrial chain of PLA is relatively mature. With the continuous advancement of biodegradable material technology worldwide, a relatively complete upstream and downstream ecological chain has been formed from lactic acid extraction, polymerization process to terminal product manufacturing. At the same time, PLA is compatible with traditional plastic processing equipment and can quickly achieve large-scale application without the need for companies to significantly replace equipment or production systems, which reduces the threshold for substitution.
However, the PLA industry still needs to overcome the following challenges:
Cost issue: At present, the production cost of PLA is higher than that of traditional plastics, and its penetration rate in price-sensitive markets is still limited.
Degradation condition restrictions: PLA degrades slowly in the natural environment and requires industrial composting facilities to decompose efficiently, which places higher requirements on the supporting treatment system.
Insufficient consumer awareness: Some end users confuse PLA with other "pseudo-degradable plastics", and market education needs to be strengthened.
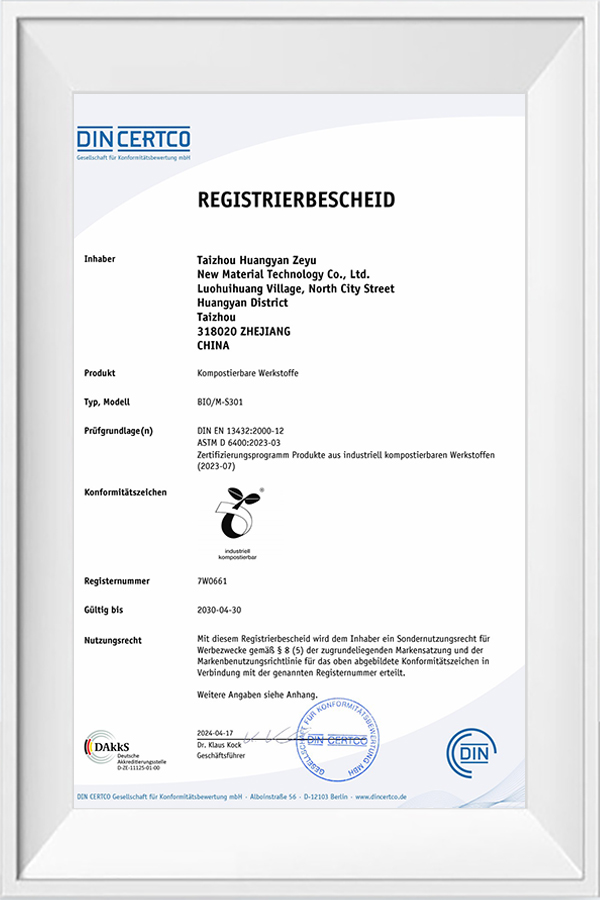
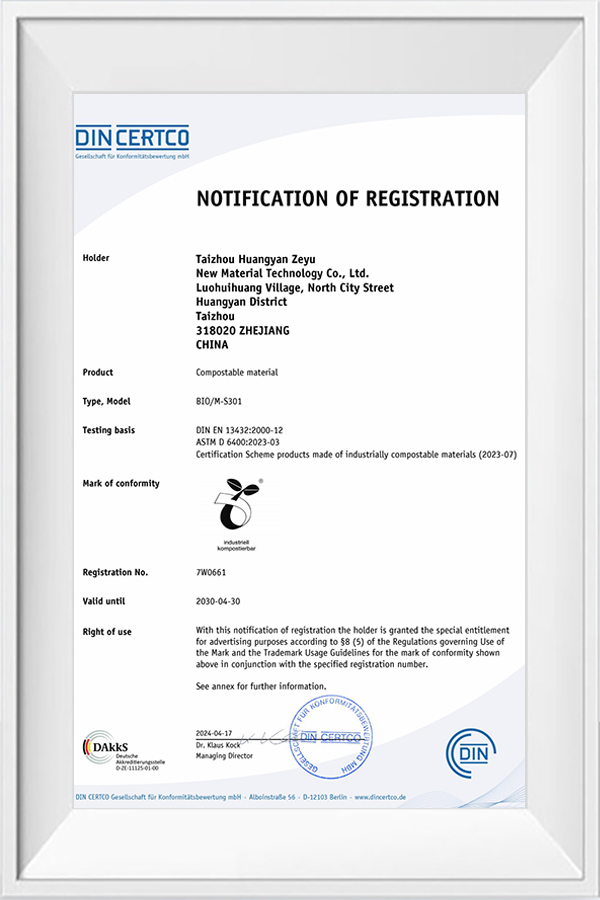
How does Taizhou Huangyan Zeyu New Material Technology Co., Ltd. promote the green transformation of the PLA industry?
As a high-tech enterprise dedicated to sustainable material innovation, Taizhou Huangyan Zeyu New Material Technology Co., Ltd. has always adhered to the core concept of "technology promotes a green future" and is committed to promoting the widespread application of biodegradable materials such as PLA throu
gh technological innovation.
The company has strong technical strength in the field of material research and development. Relying on a senior R&D team and mature process routes, it can develop PLA modified products that meet the balance of performance, cost and degradability for different application scenarios. For example, the PLA-based blended materials developed by the company have both high toughness and high transparency, and are widely used in product systems such as blown film, injection molding, and blister molding.
Taizhou Huangyan Zeyu New Material Technology Co., Ltd. attaches great importance to sustainable development goals and clearly puts forward the corporate commitment of "providing global customers with greener and more sustainable raw material options through material innovation". The company continuously invests in R&D resources to continuously optimize the performance of PLA products, while reducing production energy consumption and carbon emissions, helping upstream and downstream companies achieve environmental protection transformation.
At the marketing level, Zeyu New Materials actively responds to the country's "dual carbon strategy" and "plastic restriction" policies, and establishes stable cooperative relationships with customers in multiple industries such as catering, retail, e-commerce logistics, etc., providing customers with one-stop environmentally friendly material solutions from raw materials to end products. Through the "industry-university-research cooperation model" with universities and scientific research institutions, Zeyu continues to introduce the most cutting-edge scientific research results and accelerate the industrialization of scientific and technological achievements.